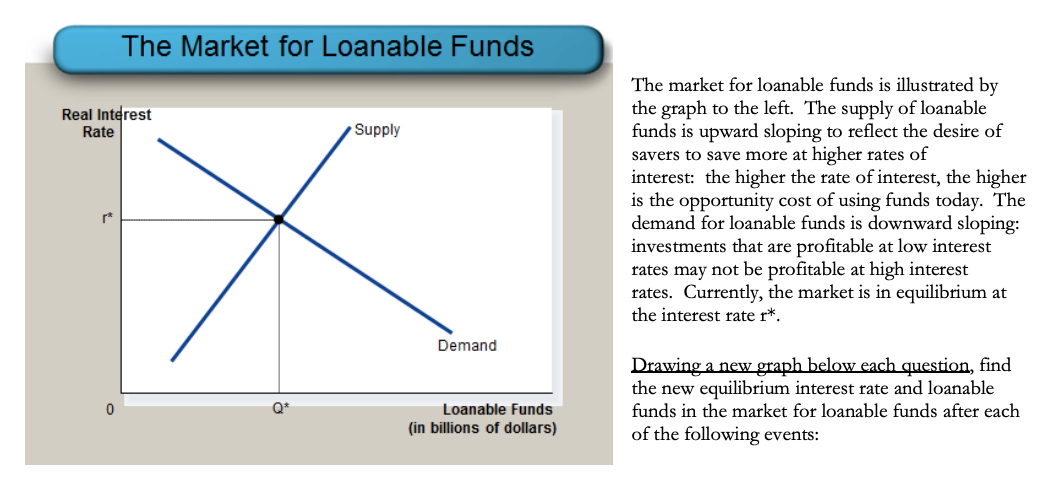
Loanable funds graph 349579-Loanable funds graph explanation
Problem 18 Hard Difficulty Draw a graph to illustrate the effect of an increase in the demand for loanable funds and an even larger increase in the supply of loanable funds on the real interest rate and the equilibrium quantity of loanable fundsPanel (a) shows the result in the loanable funds market—a shift in the demand curve for loanable funds from D1 to D2 and an increase in the interest rate from r1 to r2 At r2, the quantity of capital demanded will be K2, as shown in Panel (b)Loanable Funds Interpretation of the IS Curve (With Diagram)!
Http Onlinecampus Fcps Edu Media2 Social Studies Ap Econ Topic42 Resources Foos Lesson42 Oa Loanable Funds Answers Pdf
Loanable funds graph explanation
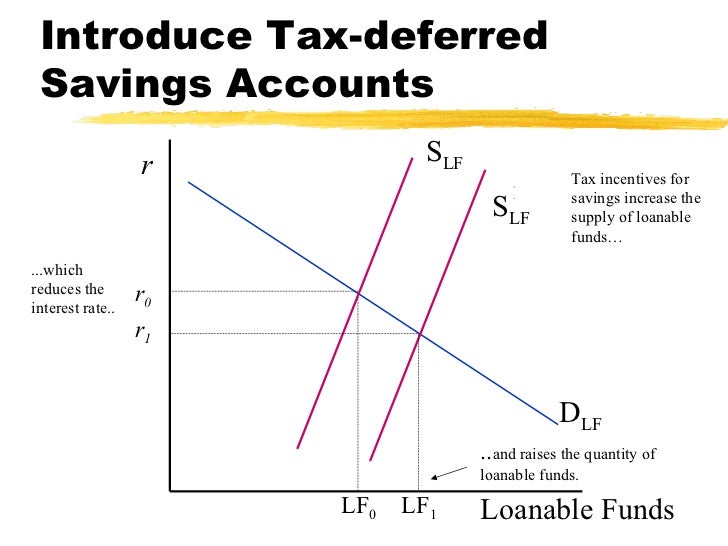
Loanable funds graph explanation-1 Loanable funds theory recognizes the importance of hoarding as a factor affecting the interest rate which the classical theory has completely overlooked 2 Loanable funds theory links together liquidity preference, quantity of money, savings and investment 3(a) Using a correctly labeled graph of the loanable funds market, show how a decision by households to increase savings for retirement will affect the real market interest rate in the short run (b) Suppose the nominal interest rate has been 6 percent with no expected inflation If inflation is now expected
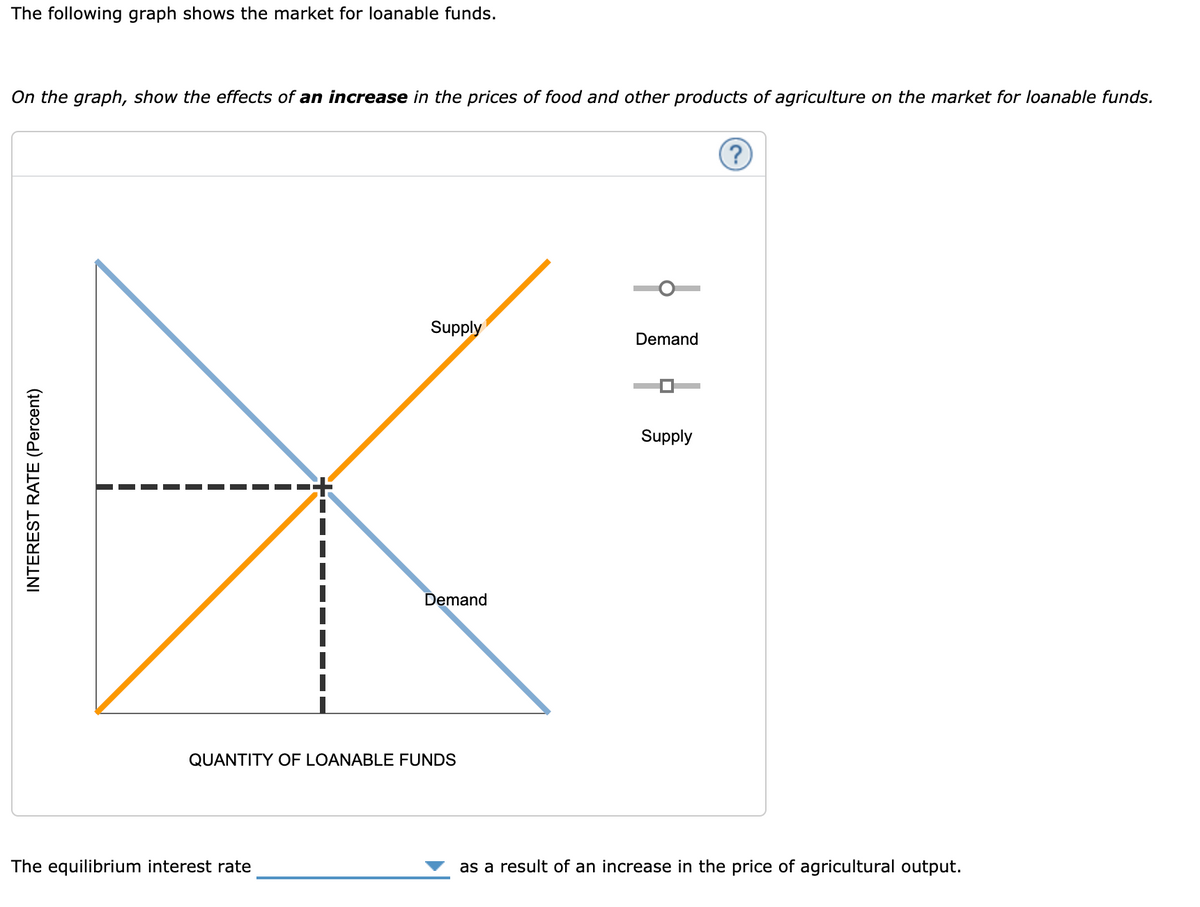



Answered The Following Graph Shows The Market Bartleby
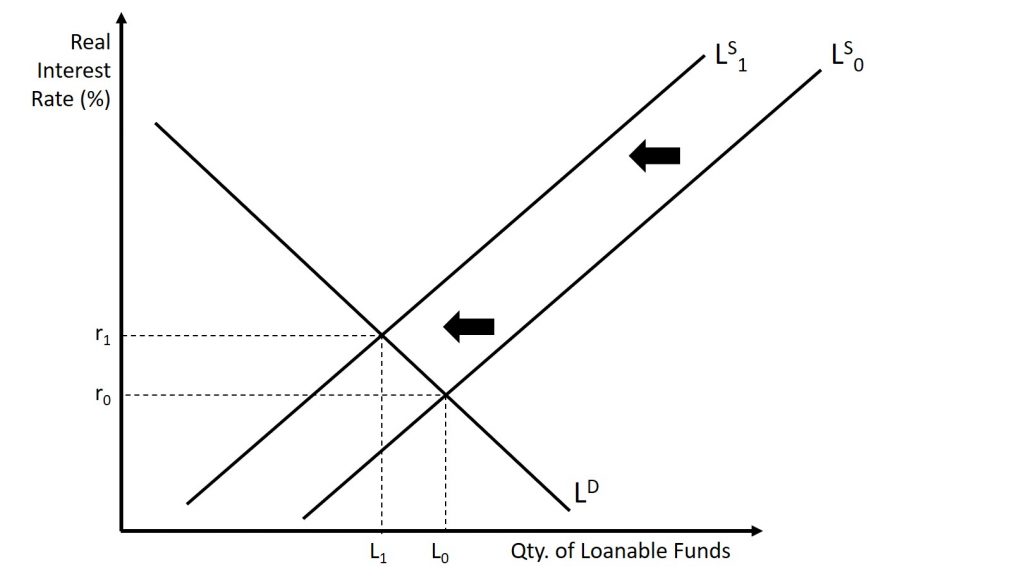
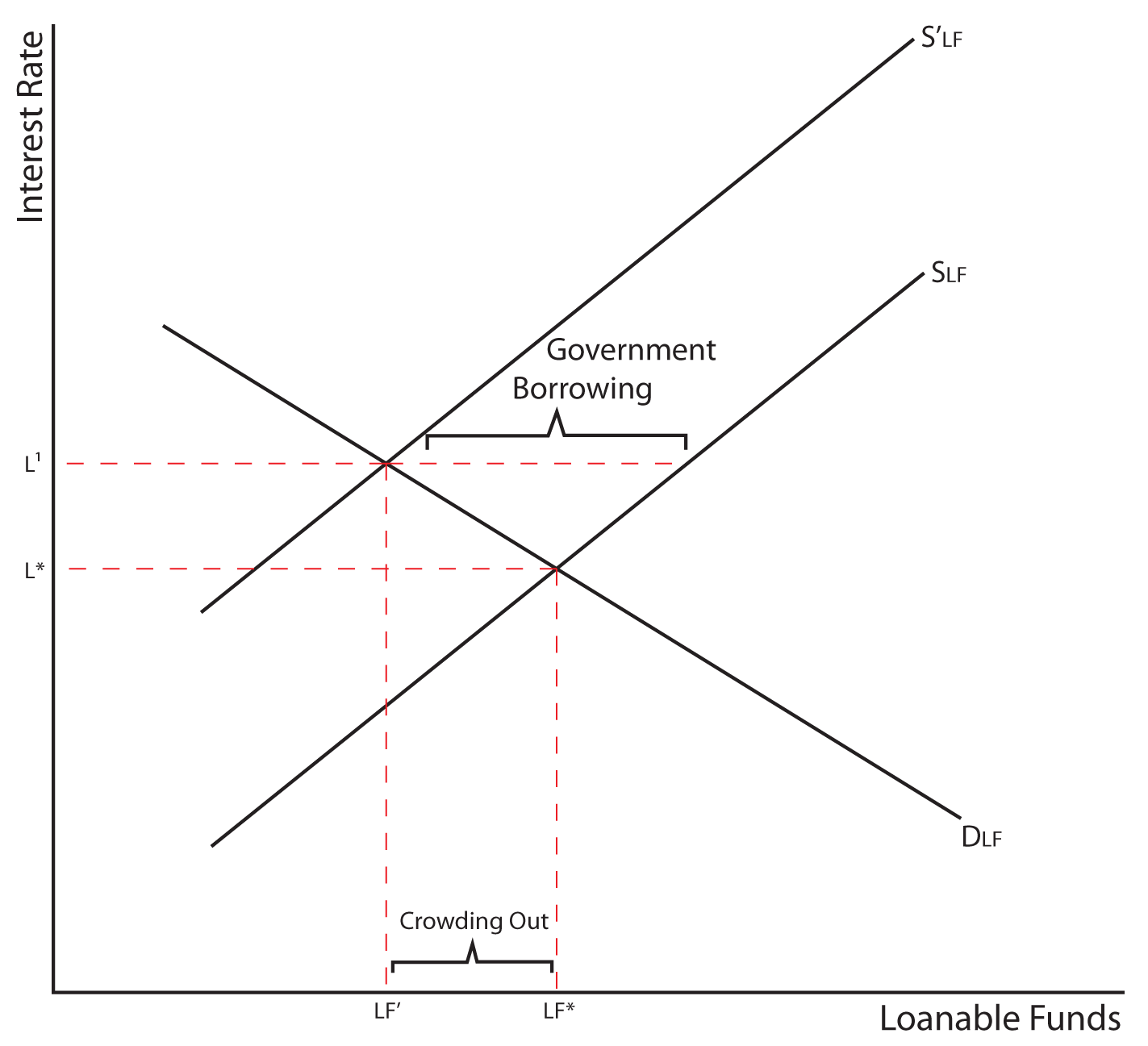
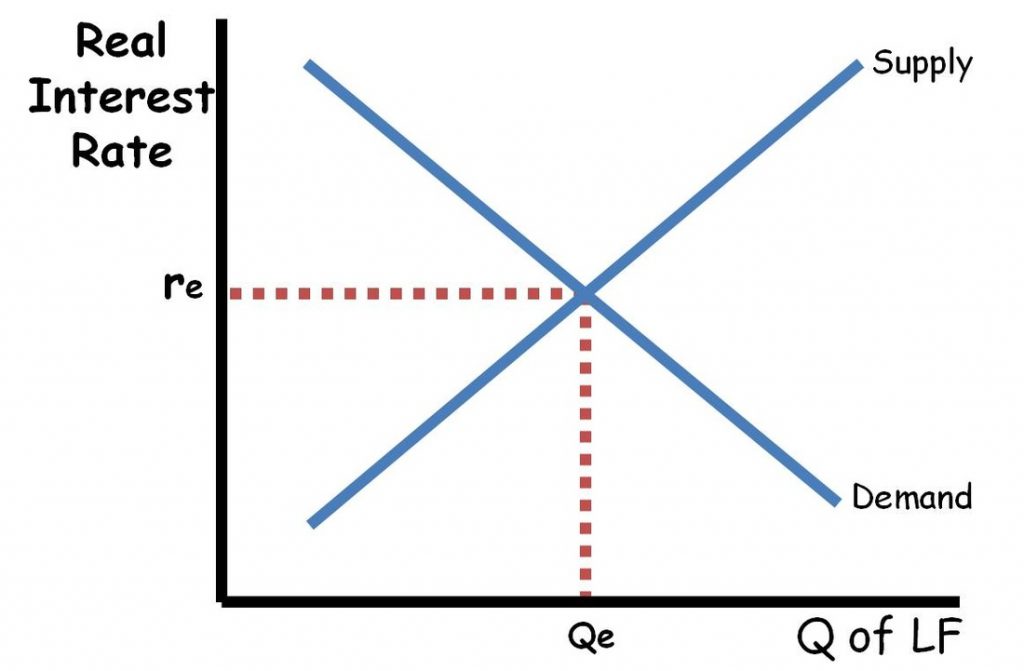
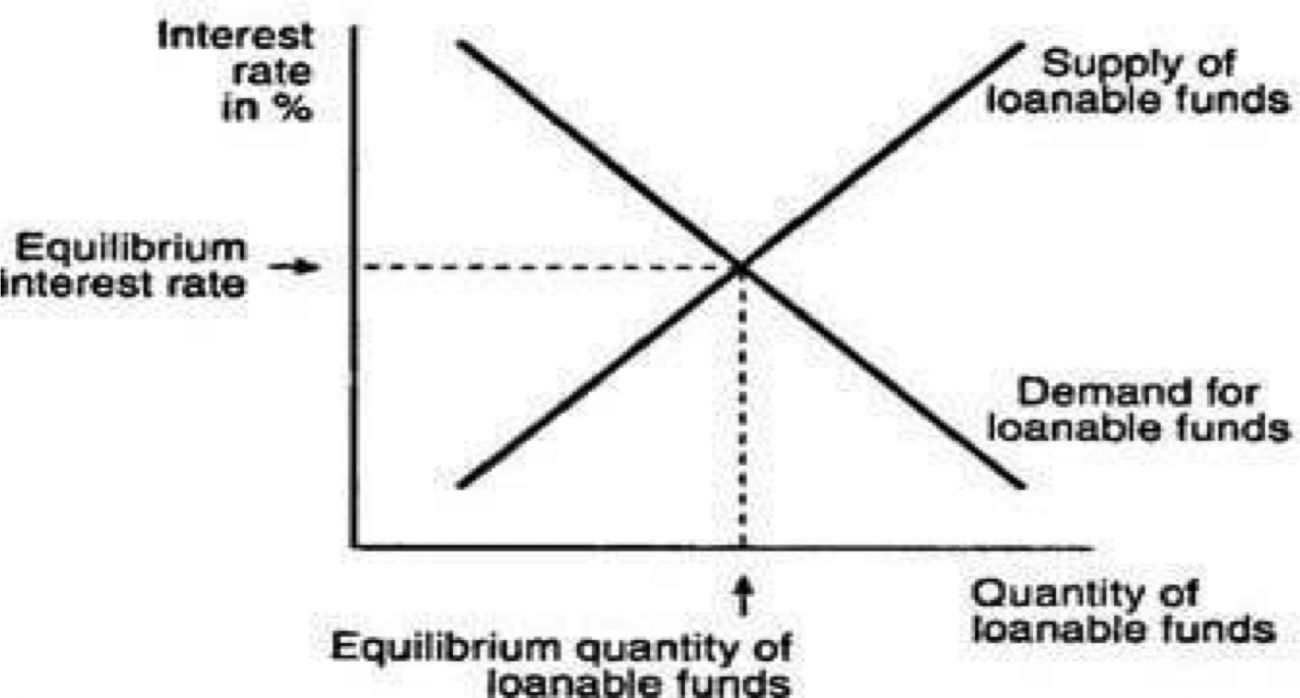
When borrowers and lenders come together, we refer to this as the loanable funds market We illustrate this by placing the demand and the supply of loanable funds on one graph The real interest rate at which the quantity demanded of loanable funds equals the quantity supplied of loanable funds •The demand for loanable funds is determined by the amount of investment businesses would like to make •If the government increases spending it causes a decrease in the supply of loanable funds (the government has taken them to deficit spend) that creates a higher interest rate AKA "Crowding out"Loanable funds Net capital outflows (NCOs, also called net foreign investment) make reference to the difference between the acquisition of foreign assets by domestic residents and the acquisition of domestic assets by nonresidents Therefore, it has to do with savings and investment (loanable funds) and foreign currency exchange
Loanable Funds Market Part I 1 Draw a correctly labeled graph showing equilibrium in the loanable funds market 2 Does each of the following affect either the supply or the demand for loanable funds, and if so, does the affected curve increase (shiftFor the loanablefunds theory to be true, therefore, it must somehow be assumed that the outstanding stock of debt does not exert any influence on interestrate determination This will be true only if either all claims are nonmarketable or, for whatever reason the claimholders (creditors) consider themselves locked into the claims they hold till the date of maturity of such claimsThe price of loanable funds is the nominal interest rate Magnitudes like expected inflation, if they have an effect, is to shift the whole demand schedule In a standard diagram, and with supply curve assumed unaffected, your answer appears strange since when a "decrease in demand" (shift to the left of the demand schedule), leads to an increase in the equilibrium price?
The loanable funds theory analyzes the ideal interest rate with a linear regression in which the quantity of loanable funds is plotted on the X axis and the real interest rate is plotted on the Y axis Then, two data sets form two lines on the graph demand for loanable funds and supply for loanable fundsThe market for loanable funds shows the interaction between borrowers and lenders that helps determine the market interest rate and the quantity of loanable funds exchanged The market for loanable funds consists of two actors, those loaning the money (savings from households like us) and those borrowing the money (firms who seek to invest the money)Update Once again I have updated this post with a few minor changes Notably, I have added to graphs illustrating a separate shift in supply and demand for loanable funds Based on discussions with readers via email, it appears that my previous graph illustrating in one diagram




Ap Econ 5 29 The Market For Loanable Funds Flashcards Quizlet




Crowding Out Video Crowding Out Khan Academy
The loanable funds market isn't just a clever solution to the problem of saving and Say's Law, it's the basic way that orthodox economists understand the financial sector in general While you'll learn more about the complexity of the financial sector and how economists understand it in later chapters, it is worth looking at one important conclusion derived from the loanable funds modelSurpluses increase the supply of loanable fundsQUANTITY (loanable funds) US Loanable Funds Market REAL INTEREST RATE S D S1 D1 QIf r1 r, r2 QIf1 QIf2 8he recession causes real interest rates to ( T increase / decrease) and foreign investors will (increase / decrease) their purchases of bonds in the United States Illustrate this change on your loanable funds graph above 9



Www Tamdistrict Org Cms Lib Ca Centricity Domain 1076 Loanable funds practice quiz Pdf



1
Loanable funds market graph shifts Similarly, you could have shifts in the supply of loanable funds Let's say, for example, the savings rate changes for some reason There's a big marketing campaign from the government or in education or in schools that say, hey, we need to Loanable funds market graph in recession The loanable funds doctrine extends the classical theory, which determined the interest rate solely by savings and investment, in that it adds bank credit Shifts of the demand for loanable funds The loanable funds market therefore recognizes the relationshipsIt is possible to suggest an alternative interpretation of the IS curve by referring to the dual role of the rate of interest in the circular flow model of national income Prima facie, the interest rate affects the supply of and demand for goods and services




As The United States Economy Moves Out Of A Recession U S Financial Investors Increase Their Purchases Of Stocks That Are Expected To Earn A Higher Rate Of Return Than They Are Currently




The Graph Shows The Market For Loanable Funds Draw A Point At The Market Equilibrium Label It 1 Suppose That The Brazilian Government Borrows The Requited Funds In The Loanable Funds Market
The Loanable Funds Market For each of the following draw a correctly labeled graph of the loanable funds market in equilibrium Based on the scenario determine whether a change in the supply or a change in the demand for loanable funds occurred Show the effects of the change on the real interest rate and quantity of loanable funds 1Demand for Loanable Funds o Demand for loanable funds used to describe the total net demand for funds by fund users o Quantity of loanable demands funds is higher as interests rates fall o More funds are demanded as interest rates decrease o Nonfinancial businesses o Interest rate cheap, borrow more o Ex Retailer TJ Maxx o Interest Rate Investment 1% $10,000 revampIt also includes the shifters that would change the supply of loanable funds or the demand for loanable funds.



Economics In Plain English A Closer Look At The Crowding Out Effect



Changes In The Demand For Capital And The Loanable Funds Market Open Textbooks For Hong Kong
The graph below depicts the market for loanable funds Complete the graph by labeling the supply and demand curves and the yaxis of the graph asked in Economics by ThorXLLoanable Funds vs Money Market whats the difference?In this one I draw and explain the graph for loanable funds and crowding out To watch the loanable funds practice video please go to the Ultimate Review Ok
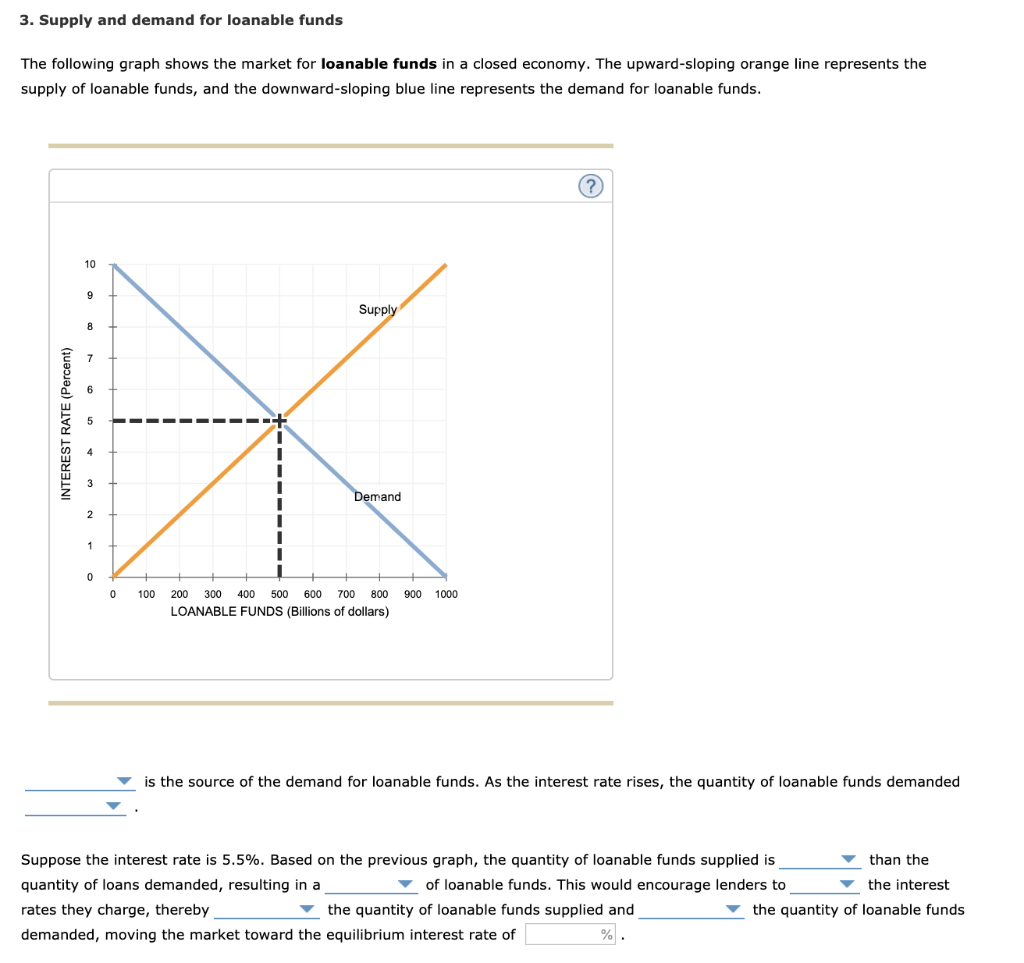



3 Supply And Demand For Loanable Funds The Following Chegg Com



Loanable Funds V Market What S The Difference Investing Post
Draw a correctly labeled loanable funds graph that shows what happens to real interest rates for each of the following situations (You will have 3 graphs) The government borrows money to fund a war Private investors become more optimistic about the economy Problem 2 On the horizontal axis of the graph, L represents the quantity of loanable funds in billions of dollars a What events could explain a shift of the demandforloanable funds curve from Dito Ba?The loanable funds market is a representation of decisions made by households and companies in relation to their lending and borrowing In most emerging countries people save little, as they are poor, and saving depend on how high the interest rates are In developed countries, people tend to save more, and thus companies




What Is The Loanable Funds Theory Critical Macro Finance



Changes In The Loanable Funds Market And The Demand For Capital Open Textbooks For Hong Kong
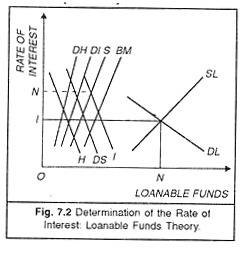
Loanable funds 1 Loanable Funds Market 2 The Market for Loans Market for loanable funds is the market in which those who want to save supply funds andDemand for Loanable Funds Shifters 1 Government Budget Deficits {direct} Borrowing in order to spend 2 All Borrowing, Loans, & Credit {direct} Applying for funds 3 Foreign Demand for Domestic Currency {direct} International exchange/converting to US dollars 4 Inflationary Expectations {inverse} Anticipation of economic performance Loanable funds is the sum total of all the money people and entities in an economy have decided to save and lend out to borrowers as an investment rather than use for personal consumption The



Economics In Plain English Loanable Funds Vs Money Market What S The Difference




Monetary Policy On The Loanable Funds As Ad Graphs Youtube
Draw a graph depicting interest rates at the quantity of loanable funds (such as the graph in figure 157) Answer the following questions regarding this graph a Explain why the supply of loanable funds is upward sloping b Explain why the demand of loanable fundsThe graph below converts the numbers in the table to an approximation of an investment schedule for US housing What we see is that the boom in housing owed loanable funds model looks at the supply of credit and the demand for credit, across term and risk structuresLoanable funds The term loanable funds is used to describe funds that are available for borrowing Loanable funds consist of household savings and/or bank loans Because investment in new capital goods is frequently made with loanable funds, the demand and supply of capital is often discussed in terms of the demand and supply of loanable funds
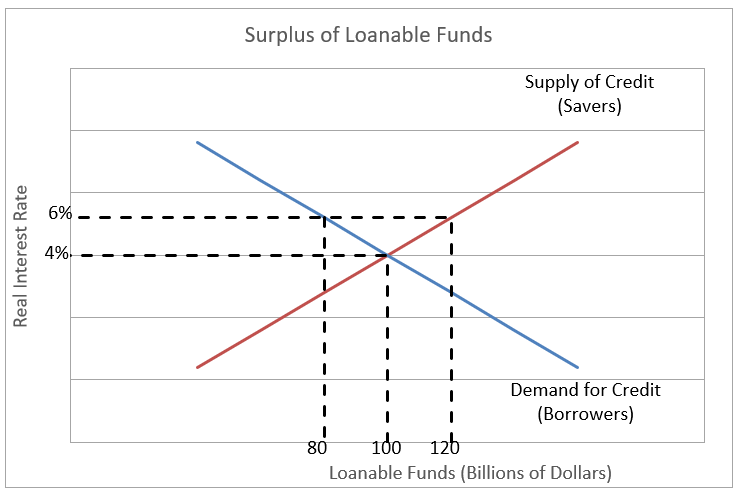



Definition Of Loanable Funds Model Higher Rock Education



Worthwhile Canadian Initiative The Loanable Funds And Other Theories
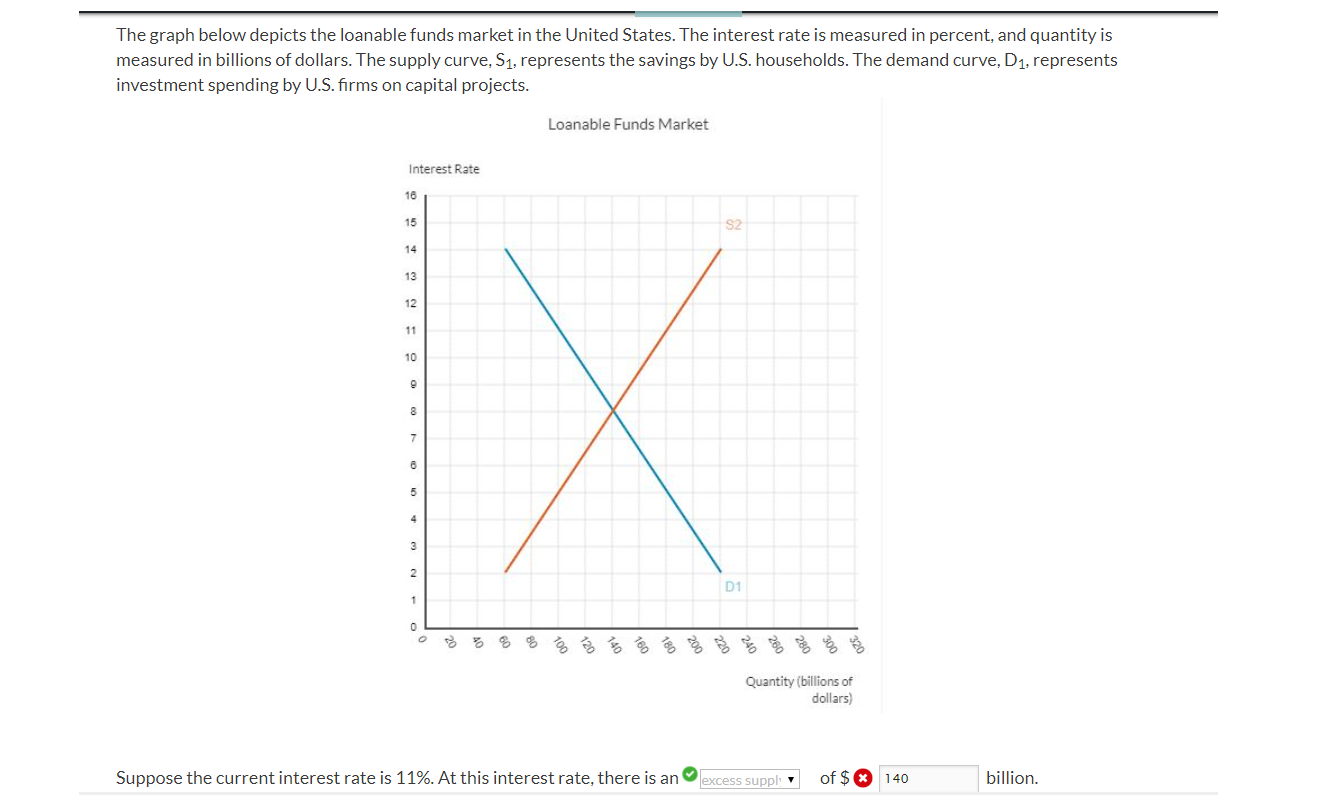
Real Interest Rate Quantity of Loanable Funds r* QLF* Demand for Loanable Funds* (Consumers/Businesses) Supply of Loanable Funds* (Consumers/Businesses/Governments) Market for Loanable Funds 7 The Demand for Loanable Funds comes From Consumers/Business/Governments Who don't have money, but want to borrow It to finance theirSurpluses decrease the demand for loanable funds The logic of this point of view is that if the government runs a deficit, it has to borrow money just like everyone else Deficits decrease the supply of loanable funds;15 Question Loanable Funds Graph Game Below you will find a 15 question review game covering every aspect of the loanable funds market It has explanations for every question so you know where you went wrong To review the content in this game, head to the Loanable Funds Market review page Suggested Minimum Score 10




The Market Of Loanable Funds With An Example Of Crowding Out Freeeconhelp Com Learning Economics Solved



Loanable Funds Policonomics
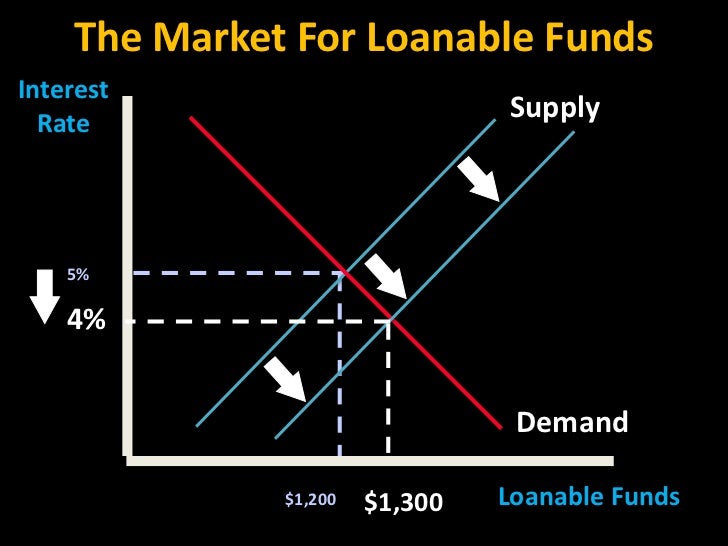
The graph below is a supply and demand graph, where four percent is the equilibrium real interest rate and $100 billion equals the loanable funds made available at four percent (The implication is that there is only one market rate Clearly this is false Loanable Funds Graph This is a document explaining the components of the loanable funds graph.Real interest rate Decreased supply Old supply X Demand Quantity of loanable funds o Real interest rate Supply Increased demand Old demand Quantity of loanable funds Old supply Increased supply о Real interest rate X Demand Quantity of loanable funds Quantity




Interest Rates And Loanable Funds



1
In macroeconomics, we refer to the amount of loanable funds supplied by the government as public savings The loanable funds' demand is determined by the interest rate The two have an inverse relationship If we plot it on a graph, the demand curve for loanable funds has a downward slope (negative)ECO 2 Topic 5 Loanable Funds Market Review True or False The purchase of a stock traded on the NYSE by an individual is considered investment spending as defined in macroeconomics True or False Negative government savings means the government runs a budget deficit True or False Government savings and national savings are the same Deficits increase the demand for loanable funds;




Principles Of Macroeconomics Study Guide




The Graph Shows The Market For Loanable Funds Draw A Point At The Market Equilibrium Label It 1 Suppose That The Brazilian Government Borrows The Requited Funds In The Loanable Funds Market
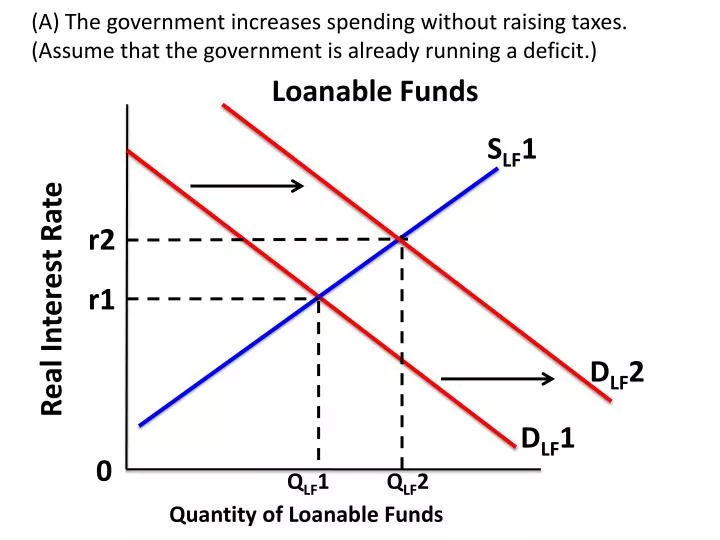
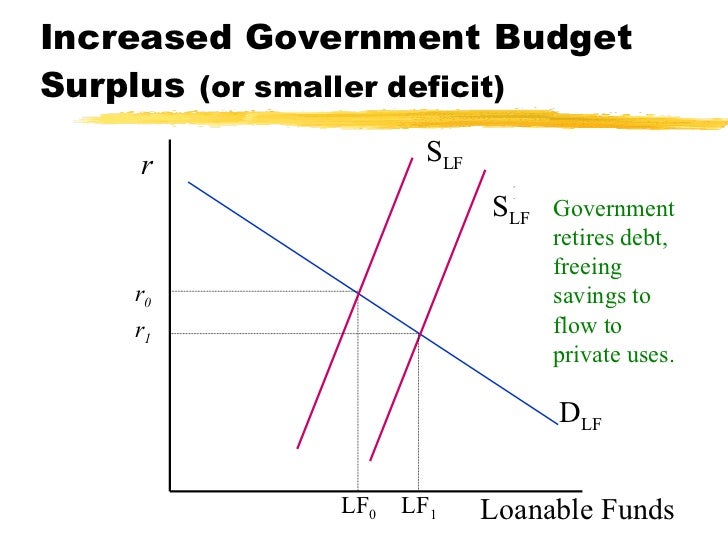
Which graph shows the effect of a government budget surplus on the loanable funds market? More loanable funds means the RIR (price of money) will decrease 14 AP Macroeconomics Exam (A) Draw a AD/AS graph showing the economy below full employment Below full employment = Recession (B) The US increases spending financed by borrowing, how does it effect the (i) Cyclical Unemployment Loanable funds graph increase in deficit spending Deficit spending occurs whenever a government's expenditures exceed its revenues over a fiscal period The accompanying graph shows the market for loanable funds in equilibrium That increased borrowing increases interest rates in the loanable funds market and crowds out private investment



Www Palmislandtraders Com Econ53 Chap3 Pdf




Loanable Funds Able Funds Demand Shifters Changes In
Then, on the graph representing the market for loanable funds, shift the demand curve, the supply curve, or both to reflect the change caused by the shift in NCO Note You will not be graded on your final placement of the curves on the graph, but you will need to shift them correctly in order to answer the questions that followUnderstanding and creating graphs are critical skills in macroeconomics In this article, you'll get a quick review of the market for loanable funds model, including what it's used to illustrate key elements of the model some examples of questions that can be answered using that model 2 The graph shows the loanable funds market when there is neither a government budget surplus nor a government budget deficit Draw a point at the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds and the equilibrium real interest rate Label it 1 Now suppose that the government has a budget deficit of $1 trillion Draw a curve that shows the effect of this deficit in the loanable funds
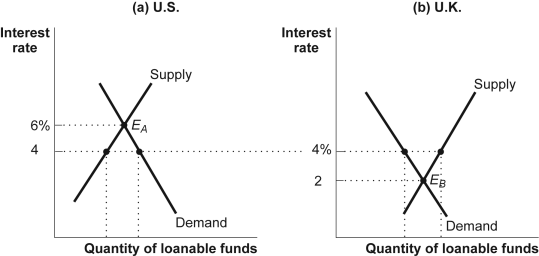



1 The Figure Shows The Loanable Funds Market For Two Chegg Com



The Market For Loanable Funds Introduction To Macroeconomics
we are used to thinking about markets for goods and services and demand and supply of goods and services and what we're going to do in this video is broaden our sense of what a market could be for by thinking about the market for loanable funds now this might seem like a very technical term loanable funds but it literally just means funds that people are supplying to



1



Www Dentonisd Org Cms Lib Tx Centricity Domain 929 Loanable Funds Market Mcfarling Fall 11 Pdf Pdf



Loanable Funds



Http Onlinecampus Fcps Edu Media2 Social Studies Ap Econ Topic42 Resources Foos Lesson42 Oa Loanable Funds Answers Pdf



Saving Investment Is The Source Of The Supply Of Chegg Com




The Market For Loanable Funds Model Article Khan Academy



Ppt Loanable Funds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Www Birdvilleschools Net Cms Lib Tx Centricity Domain 4466 Unit 5 exam review key Pdf



The Market For Loanable Funds Course Hero




The Weekend Quiz April 28 29 18 Answers And Discussion Bill Mitchell Modern Monetary Theory




Loanable Funds Market Graph



The Market For Loanable Funds




The Loanable Funds Market And Crowding Out Macro Topic 4 7 Youtube




The Market For Loanable Funds Model Article Khan Academy



The Market For Loanable Funds Real Interest Rate Chegg Com
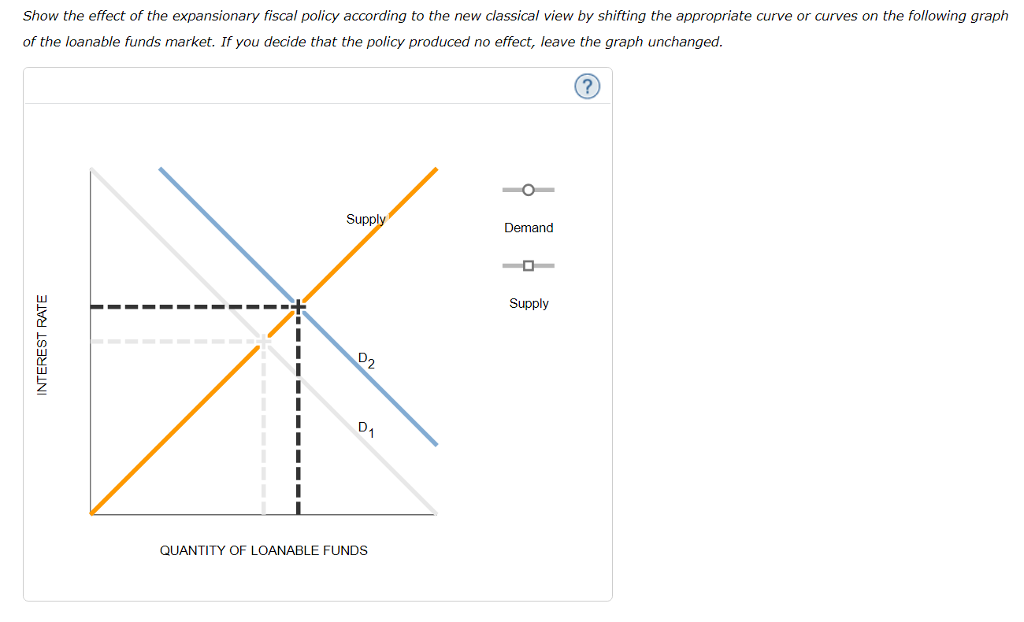



5 New Classical View Suppose Chegg Com



Economics In Plain English Loanable Funds Vs Money Market What S The Difference




Q The Accompanying Graph Shows The Market For Chegg Com




Loanable Funds Market Module 29 Market For Loanable




Capital Loanable Funds Interest Rate




Loanable Funds Honors Government Ap Macroeconomics Class
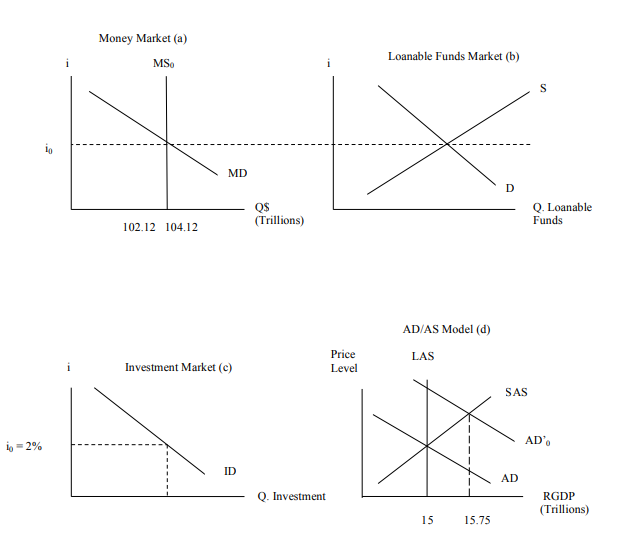



Use The Graphs Below To Illustrate And Explain Each Chegg Com



Answered Is The Source Of The Demand For Bartleby
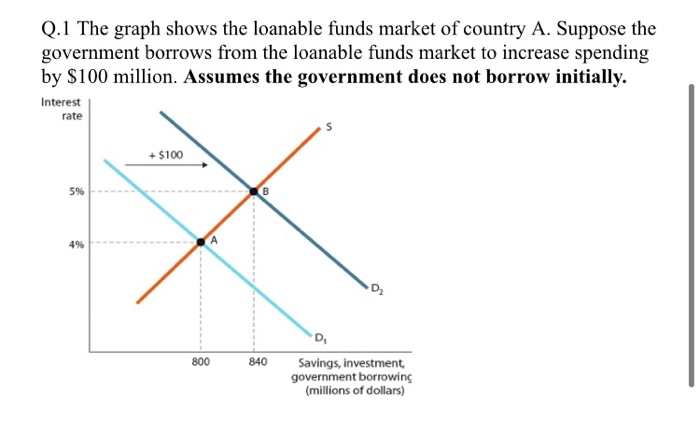



Q 1 The Graph Shows The Loanable Funds Market Of Chegg Com
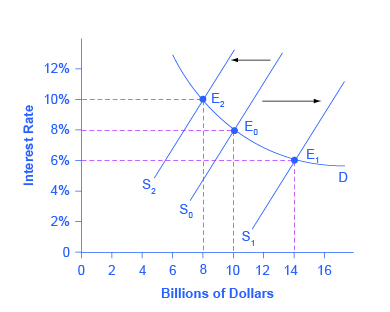



The Loanable Funds Market Principles Of Economics Scarcity And Social Provisioning 2nd Ed



Nanopdf Com Download Chapter 23 5aea23cde5c55 Pdf
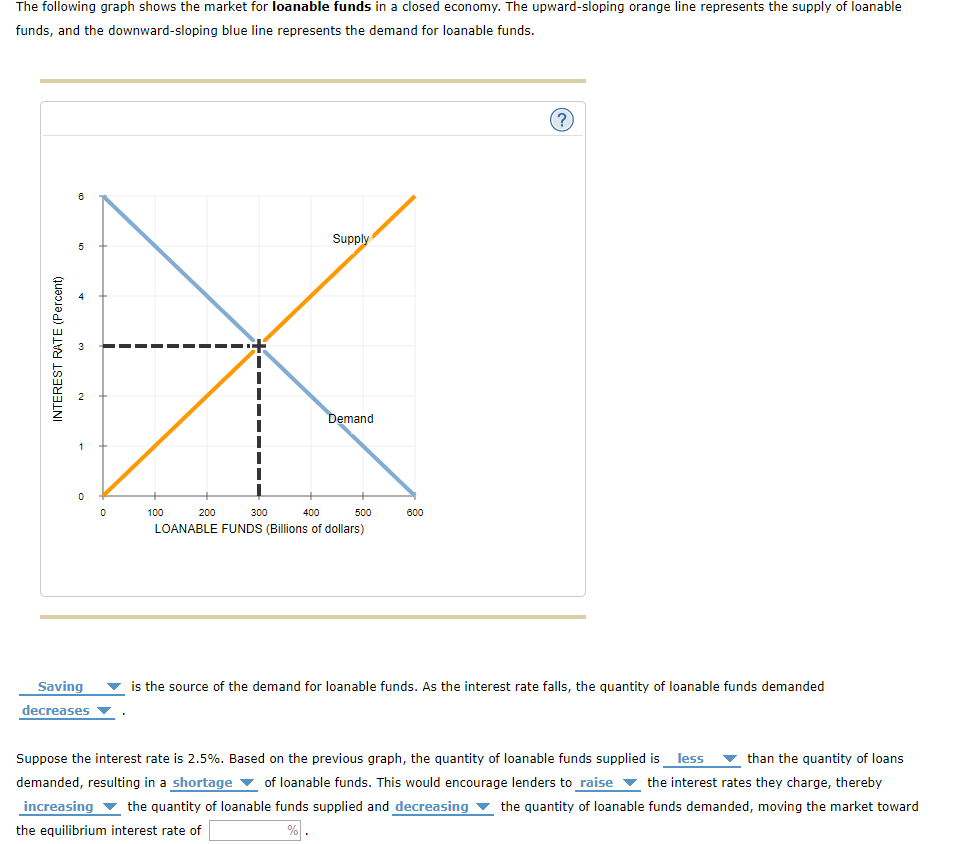



Supply And Demand For Loanable Funds The Following Chegg Com




New Mmt Graph Not Loanable Funds Greg Hannsgen S Economics Blog



Apcentral Collegeboard Org Pdf Ap19 Apc Macroeconomics Q3 Set 1 Pdf




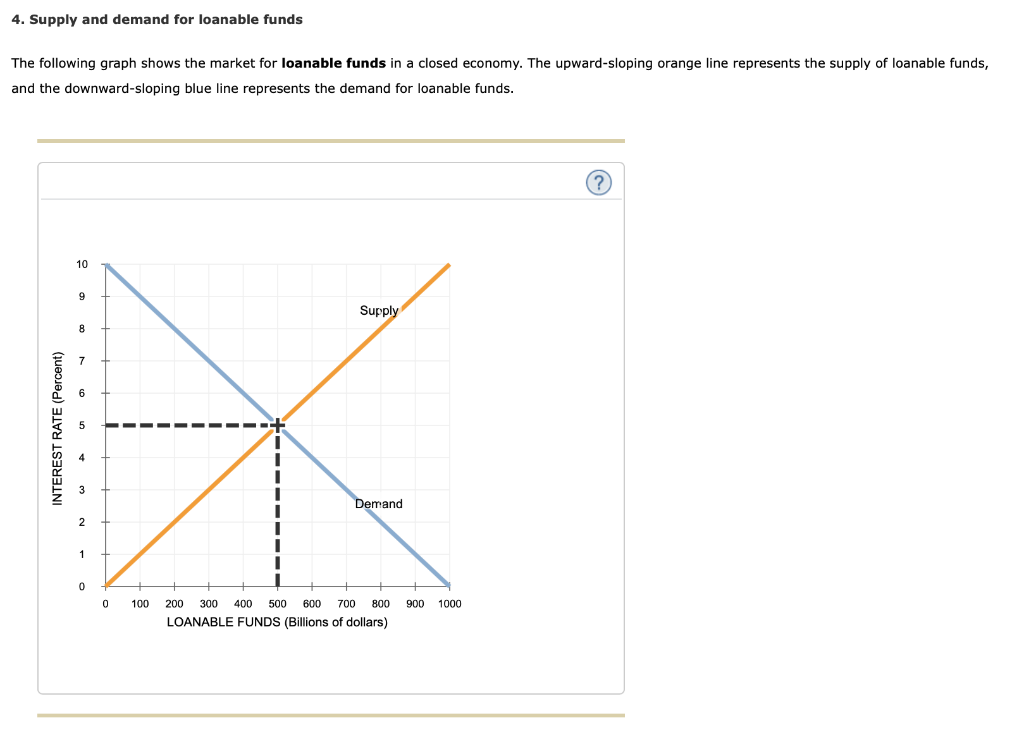
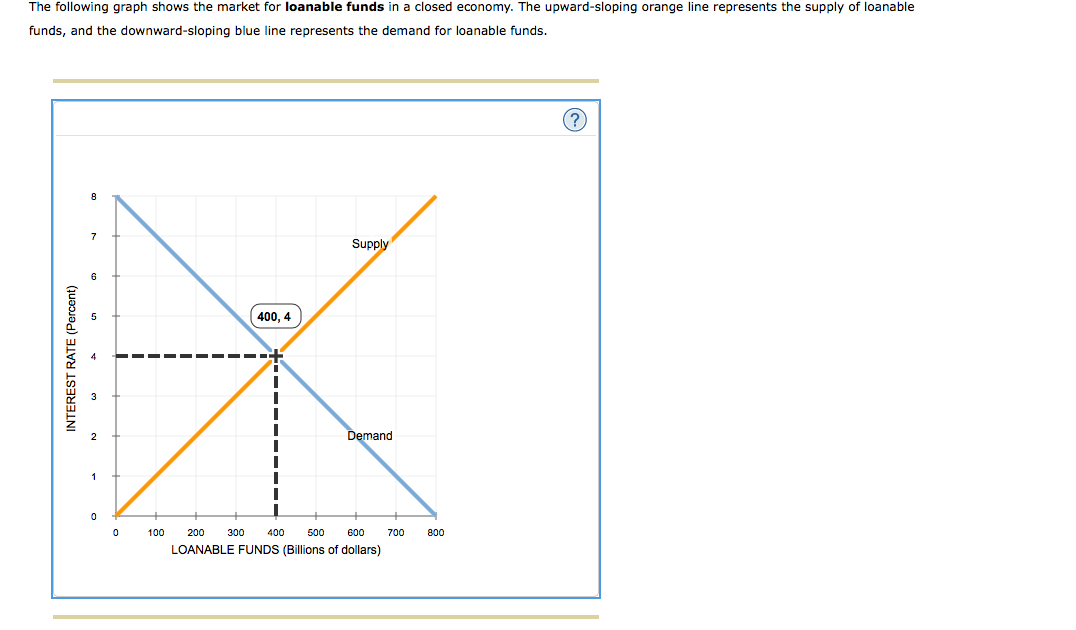
The Graph Given Below Shows The Market For Loanable Funds In A Closed Economy The Upward Sloping Orange Line Represents The Supply Of Loanable Funds And The Downward Sloping Blue Line Represents The Demand




Effects Of An Expected Increase In The Inflation Rate On The Market For Loanable Funds Economics Stack Exchange




What Is The Relationship Between The Demand For Loanable Funds And Investment Economics Stack Exchange




Macroeconomics Graphs Ap Economics Mr Bordelon Simple Circular




The Following Graph Shows The Market For Loanable Funds In A Closed Economy The Upward Sloping Orange Homeworklib
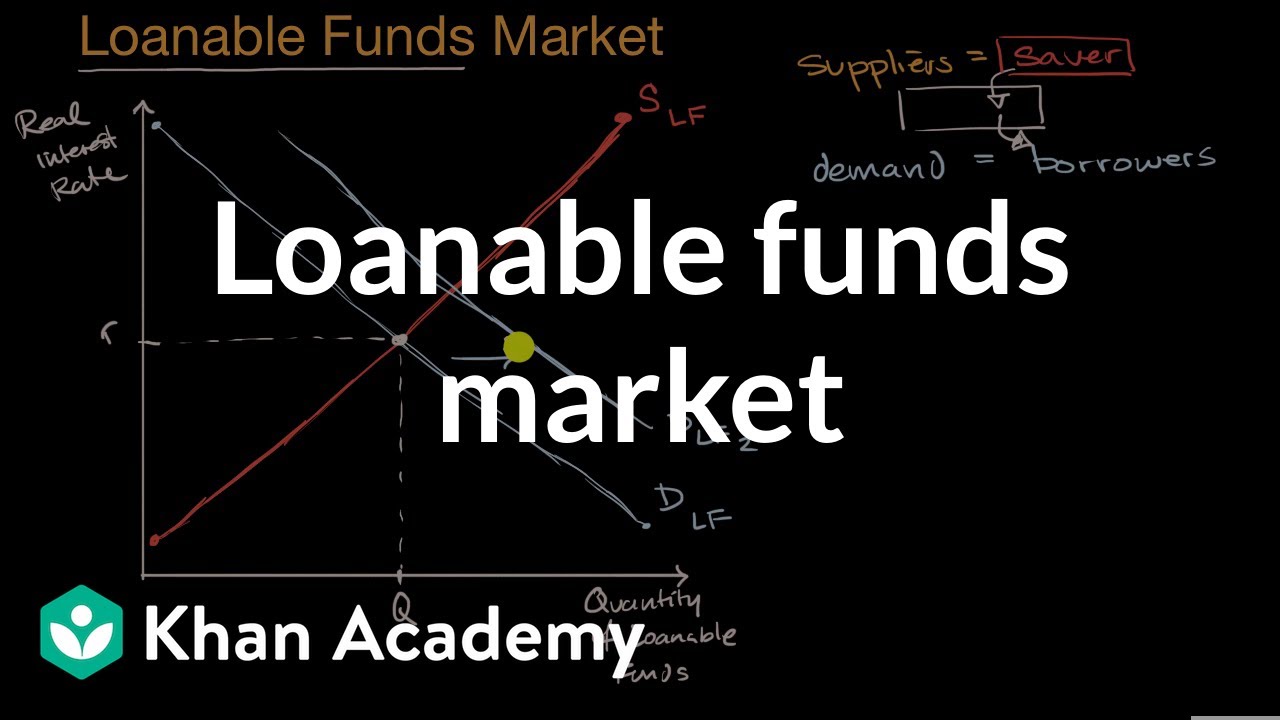



Loanable Funds Market Video Khan Academy



Econ 151 Macroeconomics



Loanable Funds Theory With Diagram



Answered Shift The Appropriate Curves To Bartleby




In A Different Scenario Suppose That The Demand And Supply Curves For Loanable Funds Shown On Homeworklib




The Following Graph Shows The Market For Loanable Chegg Com
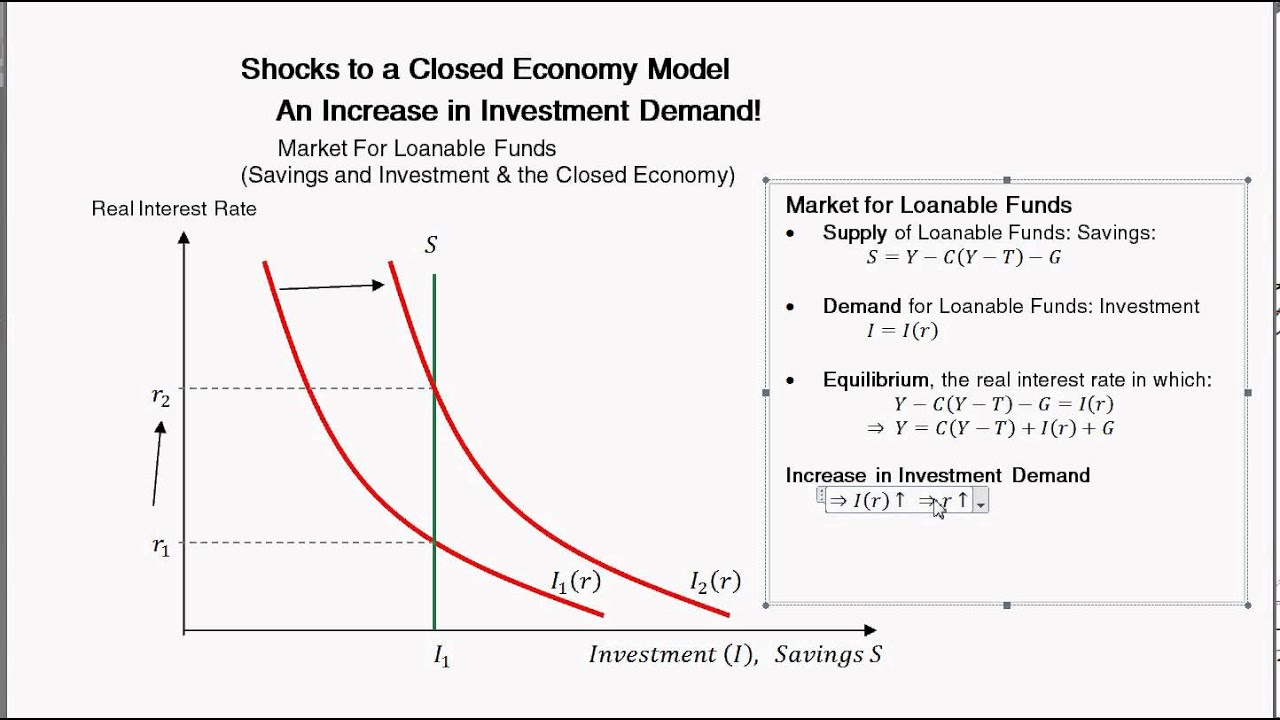



Change In Investment Demand And The Loanable Funds Market Intermediate Macroeconomics Youtube




Foreign Exchange Markets Impact On The Loanable Funds And Money Market Graphs Youtube




Answered The Following Graph Shows The Market Bartleby



What To Know About Loanable Funds By Test Day Reviewecon Com



Supply And Demand Of Loanable Funds With Explanations




Use The Graph Of The Loanable Funds Market Below If Chegg Com



Apcentral Collegeboard Org Pdf Ap19 Apc Macroeconomics Q3 Set 1 Pdf



Loanable Funds Policonomics



Solved Real Interest Rate 796 Supply 696 Iii 59 49 39 796 19 Demand 3 6 9 12 15 18 21 Quantity Of Loanable Funds In Billions Of Dollars Course Hero



Worthwhile Canadian Initiative The Loanable Funds And Other Theories




The Market For Loanable Funds Model Article Khan Academy



Solved 1 Let S Think About The Market For Loanable Funds One Of Its Examples Is The Market For Housing Loans Let S Analyze How Covid 19 Affects Course Hero



Module 29 The Market For Loanable Funds




Loanable Funds



Macroeconomics Loanable No Bull Economics Lessons



Economics In Plain English A Closer Look At The Crowding Out Effect



Economics In Plain English Loanable Funds Vs Money Market What S The Difference



Using The Loanable Funds Theory Show In A Graph How The Following Events Will Affect The Supply And Demand For Loans And The Equilibrium Nominal Interest Rate A Recent Signs Of Economic



Www Palmislandtraders Com Econ53 Chap3 Pdf



Market For Loanable Funds Activity




A The Government Increases Spending Without Raising Taxes Assume That The Government Is Already Running A Deficit Loanable Funds D Lf 2 Real Interest Ppt Download



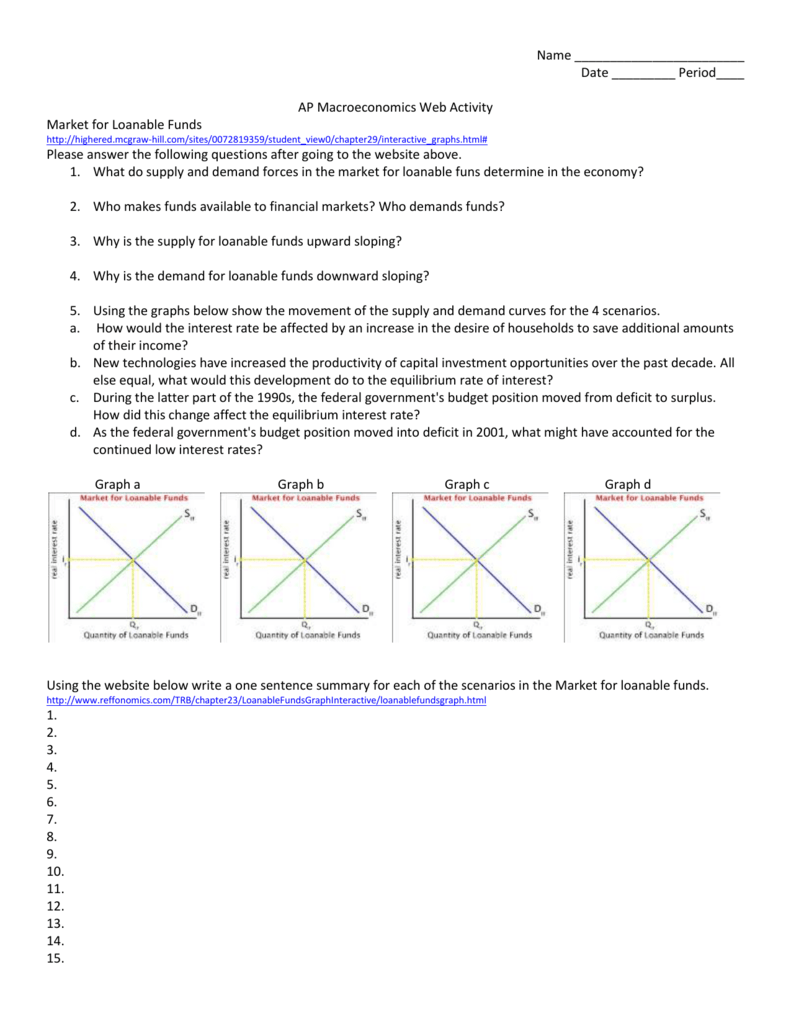
The Graph Below Depicts The Loanable Funds Market In Chegg Com




Econowaugh Ap Nominal Vs Real Money Supply Vs Loanable Funds




Using A Graph Representing The Market For Loanable Funds Show And Explain What Happens To Interest Homeworklib




The Loanable Funds Fallacy Real World Economics Review Blog




Shifting The Demand Curve For Loanable Funds Youtube




3 Supply And Demand For Loanable Funds The Following Graph Shows The Market For Homeworklib



Http Www Socsci Uci Edu Mouyang Ps b Answer key4 Pdf
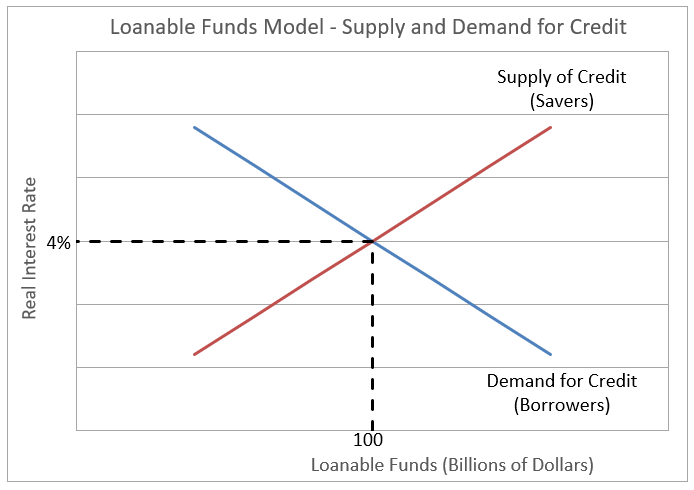



Definition Of Loanable Funds Model Higher Rock Education



Worthwhile Canadian Initiative The Loanable Funds And Other Theories




Reading Loanable Funds Macroeconomics




Reading Loanable Funds Macroeconomics
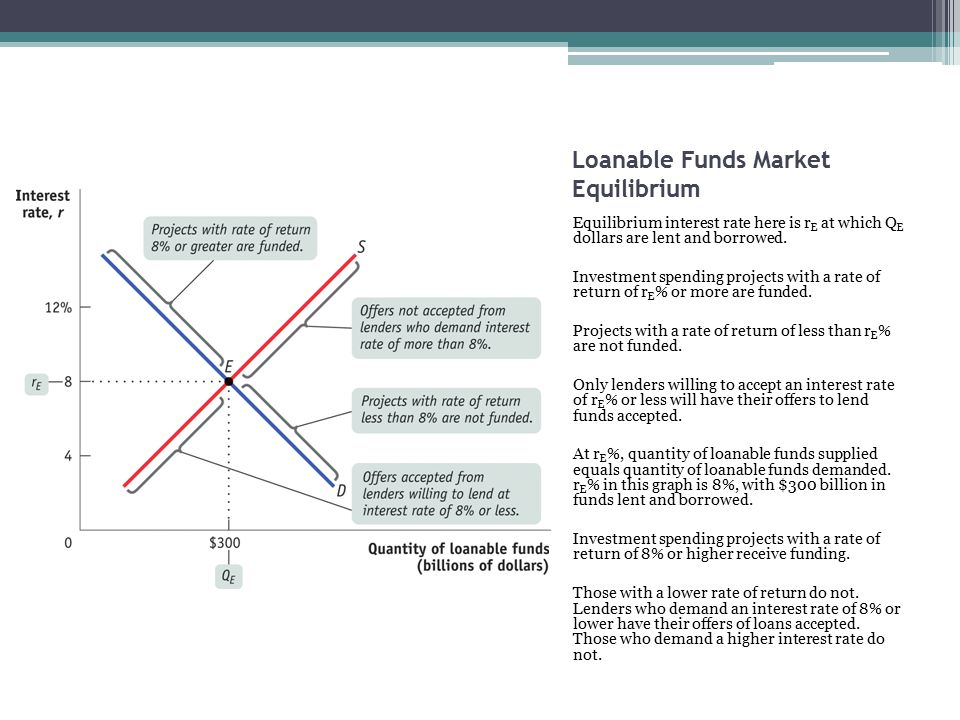



Financial Sector Loanable Funds Market Ppt Video Online Download



1



Www Palmislandtraders Com Econ53 Chap3 Pdf



Loanable Funds Policonomics



Loanable Funds




Solved 5 The Market For Loanable Funds And Government Policy The 1 Answer Transtutors



コメント
コメントを投稿